Reported Conditions for Peace: Putin’s Terms for Ukraine – By Dr. Harold Gunatillake

Image Source : cdn.images.express.co.uk
Analysis of the Anchorage Discussion and Its Implications
Overview
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has significantly redefined international relations, resulting in widespread conflict, human suffering, and geopolitical instability. Diplomatic efforts—both public and private—have been unsuccessful in securing a lasting resolution, as the stakes are high and positions remain entrenched.
The Anchorage Meeting: Putin’s Reported Proposal
Recent reports indicate that Russian President Vladimir Putin conveyed his peace proposals directly to former U.S. President Donald Trump during a meeting in Anchorage. According to these reports, Putin’s conditions extend beyond a simple ceasefire, proposing terms for a comprehensive peace agreement.
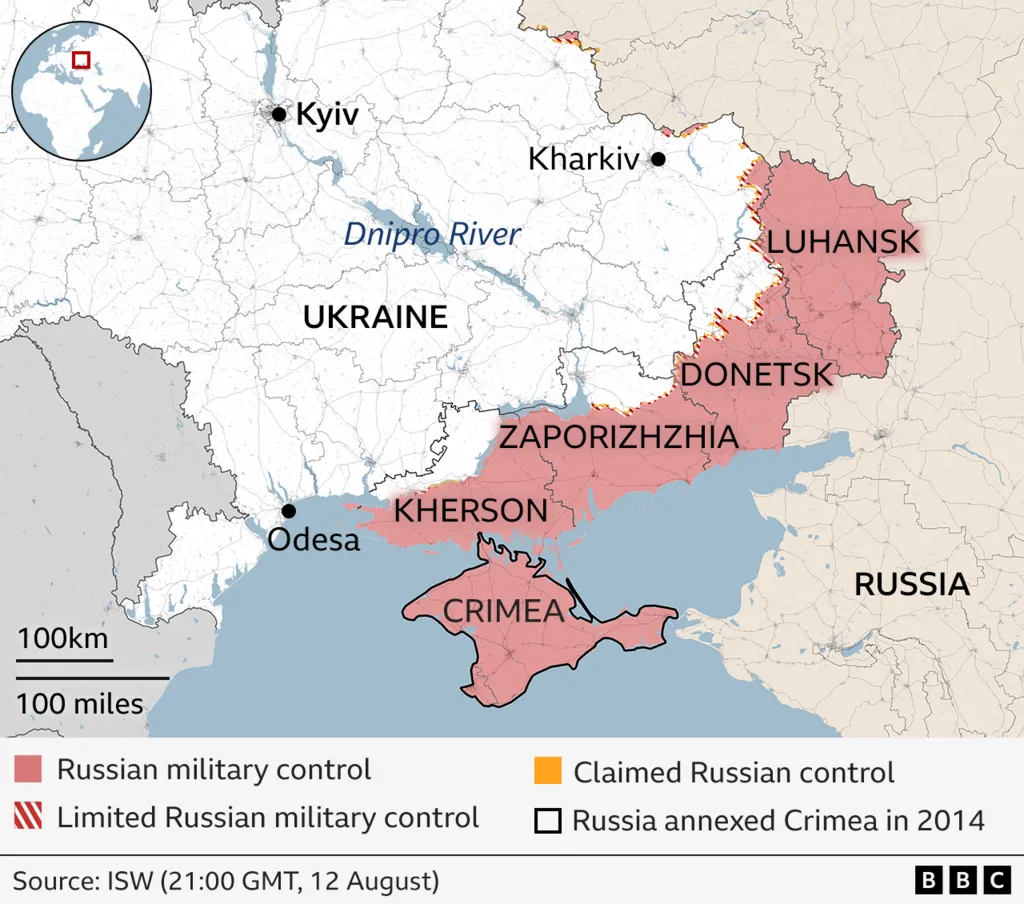
Image Source : bbc.com
Key Conditions
- Ukraine must cede Donbas and Crimea: Putin reportedly demands that Ukraine relinquish control of the Donbas region and Crimea, both of which have been central flashpoints since
- No further aggression, guaranteed in writing: In exchange, Putin offers a written promise not to attack or occupy any additional territories in Ukraine or
The Donbas region, situated in eastern Ukraine, has experienced intense conflict since 2014, after Russia annexed Crimea and the onset of separatist hostilities. The annexation of Crimea, widely condemned by the international community, continues to be a matter of substantial dispute. For Ukraine, both regions are vital to national identity; for Russia, control over these areas holds strategic and historical significance.
Analysis of the Proposal
Putin’s terms embody a maximalist negotiating stance, aiming to formalise Russia’s territorial acquisitions while ostensibly limiting future Russian expansionism. From the perspectives of Ukraine and the West, these conditions are profoundly contentious and, to many, wholly unacceptable.
The prospect of Ukraine relinquishing substantial regions that are culturally and economically vital is viewed as a surrender of sovereignty and a reward for military aggression.
Moreover, scepticism abounds regarding the value of a “written promise” from the Kremlin. Russia’s prior commitments—most notably the Budapest Memorandum of 1994, which guaranteed Ukraine’s territorial integrity—were ultimately disregarded. As such, the credibility of any new assurance from Putin is widely questioned, with many commentators suggesting such promises are of little practical value.
Vladimir Putin and Russian officials have offered various rationales for their actions, from historical claims over Crimea to fears of NATO encroachment. The Kremlin has dismissed the Budapest Memorandum as irrelevant, arguing that the 2014 revolution represented a break in Ukrainian state continuity and that Russia was not obligated to respect the new government.
Such arguments have garnered limited international support. The majority of observers interpret the annexation and intervention in eastern Ukraine as strategic manoeuvres intended to reaffirm Russian influence, destabilise Ukraine’s westward progression, and contest the post-Cold War international order.
Zelensky has dismissed any possibility of Ukrainian forces withdrawing from the eastern regions as part of a peace agreement.
Furthermore, according to a recent opinion poll conducted by the Kyiv International Institute of Sociology, 82 per cent of Ukrainians oppose Russia’s demands to cede territory.
Conclusion
The terms outlined by Putin in Anchorage underscore the ongoing challenges of the Ukraine conflict. Asking Ukraine to give up Donbas and Crimea in exchange for peace shows the deep divisions and the slim chances for a compromise that everyone can agree on. Ultimately, the outcome of negotiations will depend on Ukraine’s determination, the unity of Western allies, and how risks and rewards are assessed when dealing with Russia—a country whose promises have often been fleeting.
End